Mitigating NTLM Relay Attacks on Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) – ADV210003 – KB5005413 – PetitPotam

Updates
2021-08-06 – Added recommendations to protect DC’s
The MS-EFSRPC protocol can be used to coerce any Windows host including Domain Controllers to authenticate to a specific destination. The designated destination then forwards the NTLM credentials to another service that is configured to accept WIA/NTLM resulting in an abuse of the services.
An attacker can target a Domain Controller to send its credentials by using the MS-EFSRPC protocol and then relaying the DC NTLM credentials to the Active Directory Certificate Services AD CS Web Enrollment pages to enroll a DC certificate. This will effectively give the attacker an authentication certificate that can be used to access domain services as a DC and compromise the entire domain.
AD CS is especially interesting as it offers role services that by default accept NTLM based authentication. The Certificate Authority Web Enrollment and the Certificate Enrollment Web Service can be abused to issue certificates by performing NTLM Relay Attacks using MS-EFSRPC, MS-RPRN or other API that offer a smilar behavior.
Microsoft has released ADV210003 and KB5005413 in response to the published POC.
Mitigations
We share the Microsoft recommended mitigations but think that it is very important to address the justification of having the affected role services and recommend the following mitigations:
Protecting your DC’s
Block outbound traffic from DC’s
Blocking connections initiated by DC to arbitrary services and hosts is an effective mitigation. DC’s should only initiate connections to well known destinations like other DC’s or hosts that are classified to be necessary for such communication. If tiering is implemented in the domain, outbound connections should be limited to tier 0 hosts and services.
Block [MS-ESFR] (EFSRPC) using RPC filters
Benjamin Delpy suggested to use RPC filters to block MS-EFSR by creating filter rules to block the known UUID’s for pipelsarpc and pipeefsrpc using the command:
netsh.exe -f block_efsr.txt
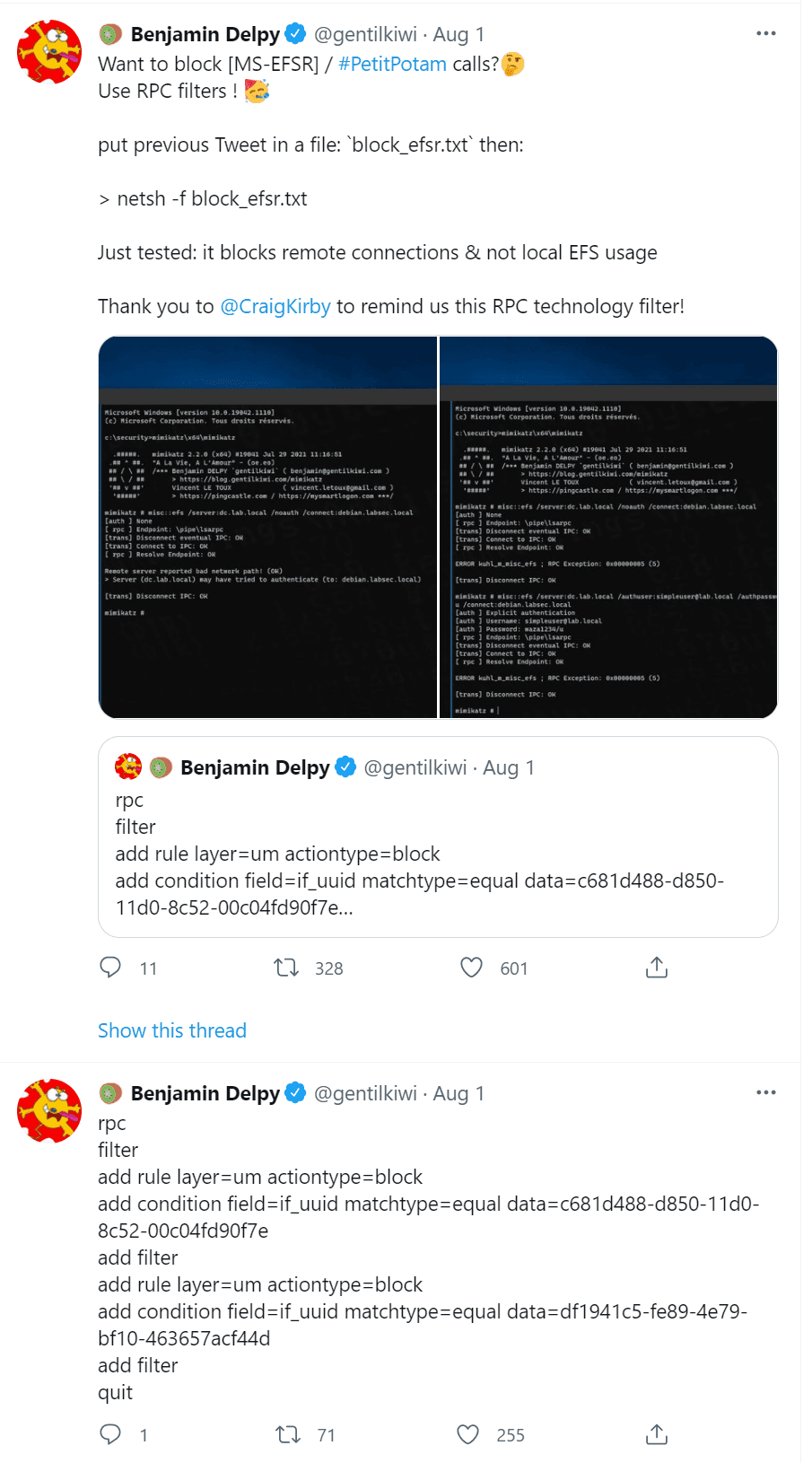
Using RPC filtering to block PetitPotam calls
The content of the suggested block_efsr.txt is
rpc filter add rule layer=um actiontype=block add condition field=if_uuid matchtype=equal data=c681d488-d850-11d0-8c52-00c04fd90f7e add filter add rule layer=um actiontype=block add condition field=if_uuid matchtype=equal data=df1941c5-fe89-4e79-bf10-463657acf44d add filter quit
Protecting/Fixing AD CS
Preferred mitigation
Remove the listed role services if not justified by a business need. In most of the cases the affected services are replaceable by other API/interfaces such as the built-in RPC interfaces.
Secondary Mitigations
If removing the affected role services is not an option we strongly advice to perform the following actions (listed in order of more secure to less secure):
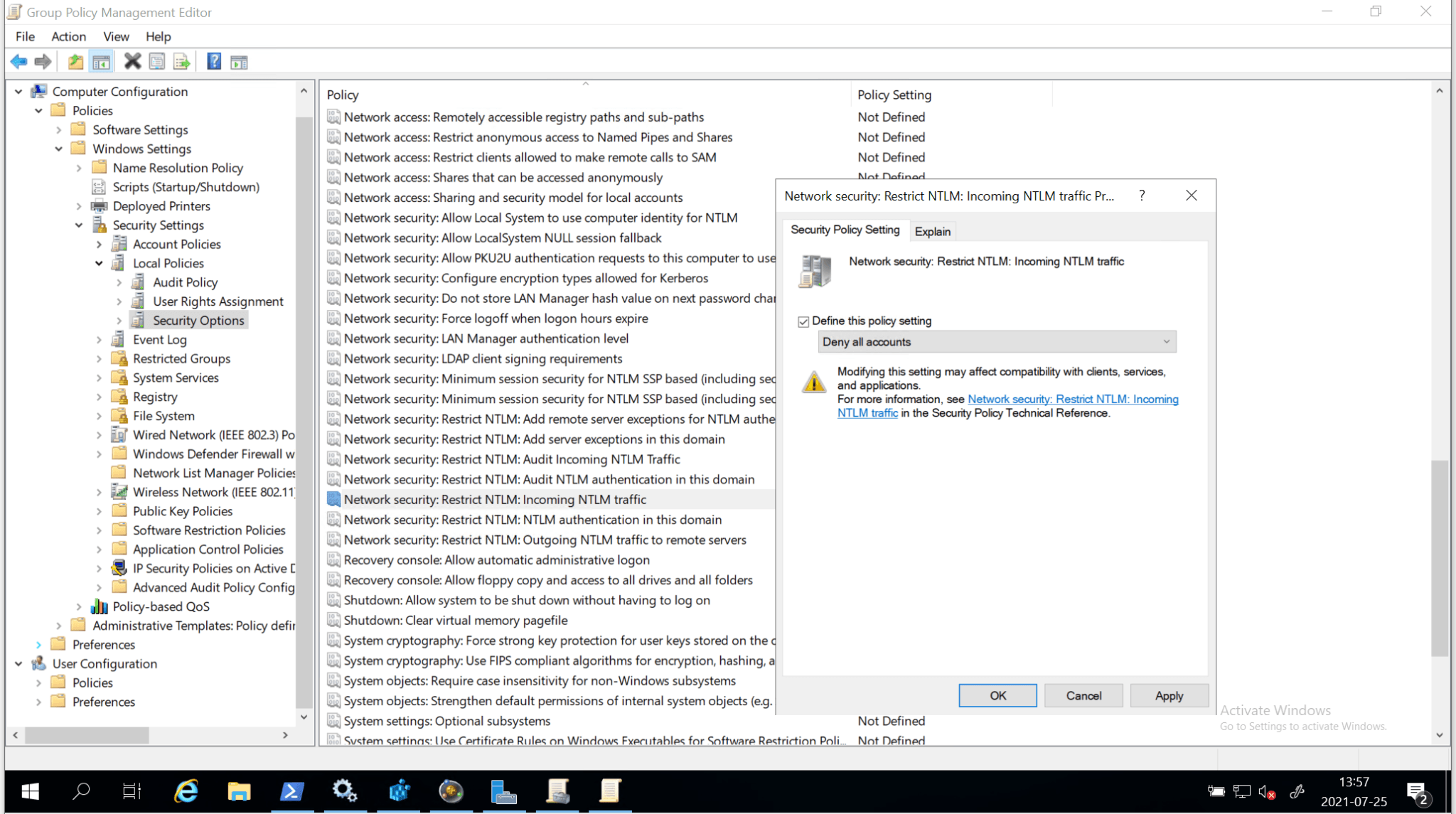
- Restrict/disable inbound NTLM authentication to the server running the role service by setting the policy “Network security: Restrict NTLM: Incoming NTLM traffic”.
- Disable/remove the NTLM provider in the Internet Information Services (IIS) running the selected role services.
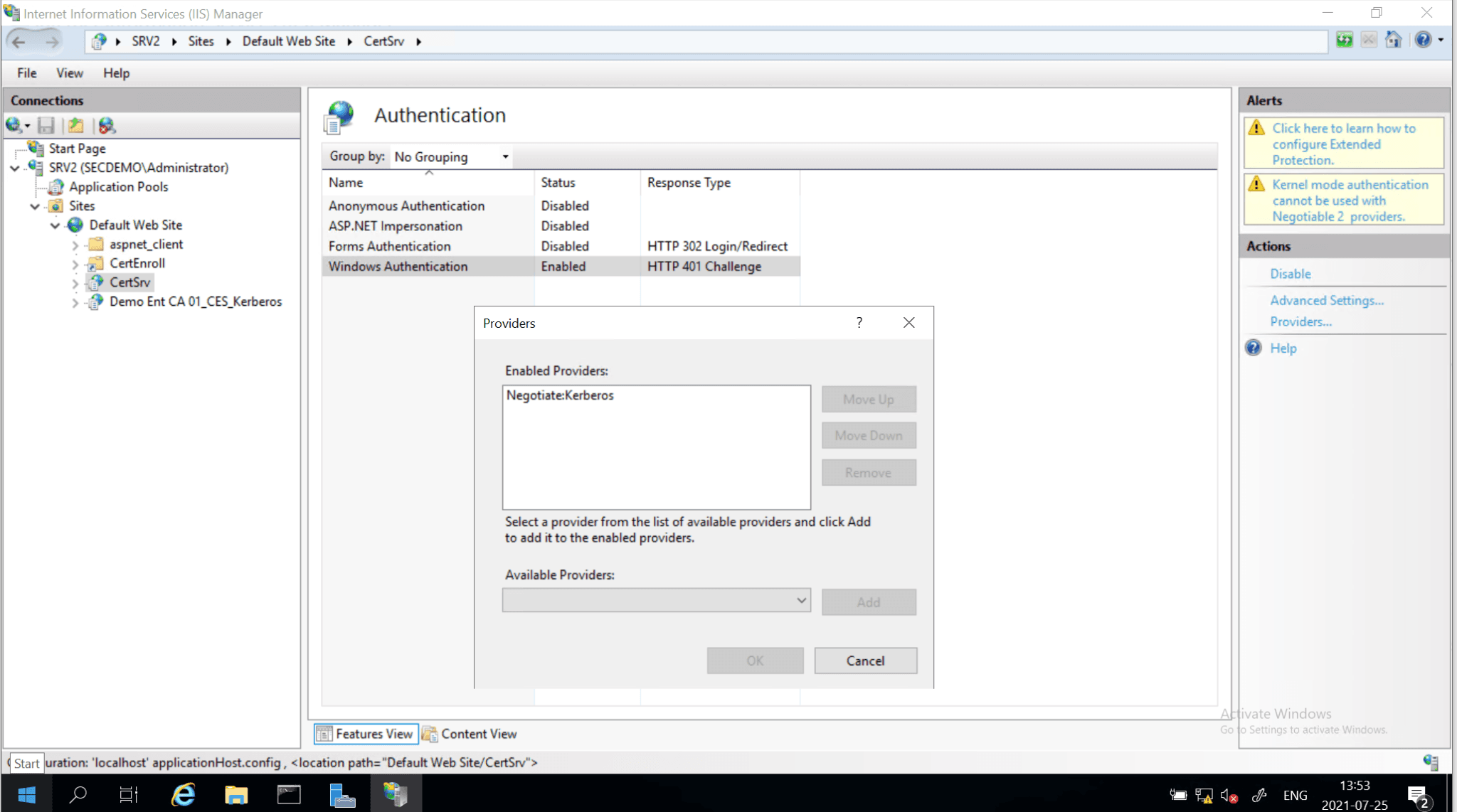
Disable NTLM – Internet Information Services (IIS)
Additional mitigations
If NTLM must remain enabled, we recommend
- Enabling Extended Protection for Authentication (EPA) And Require TLS on the selected role services.
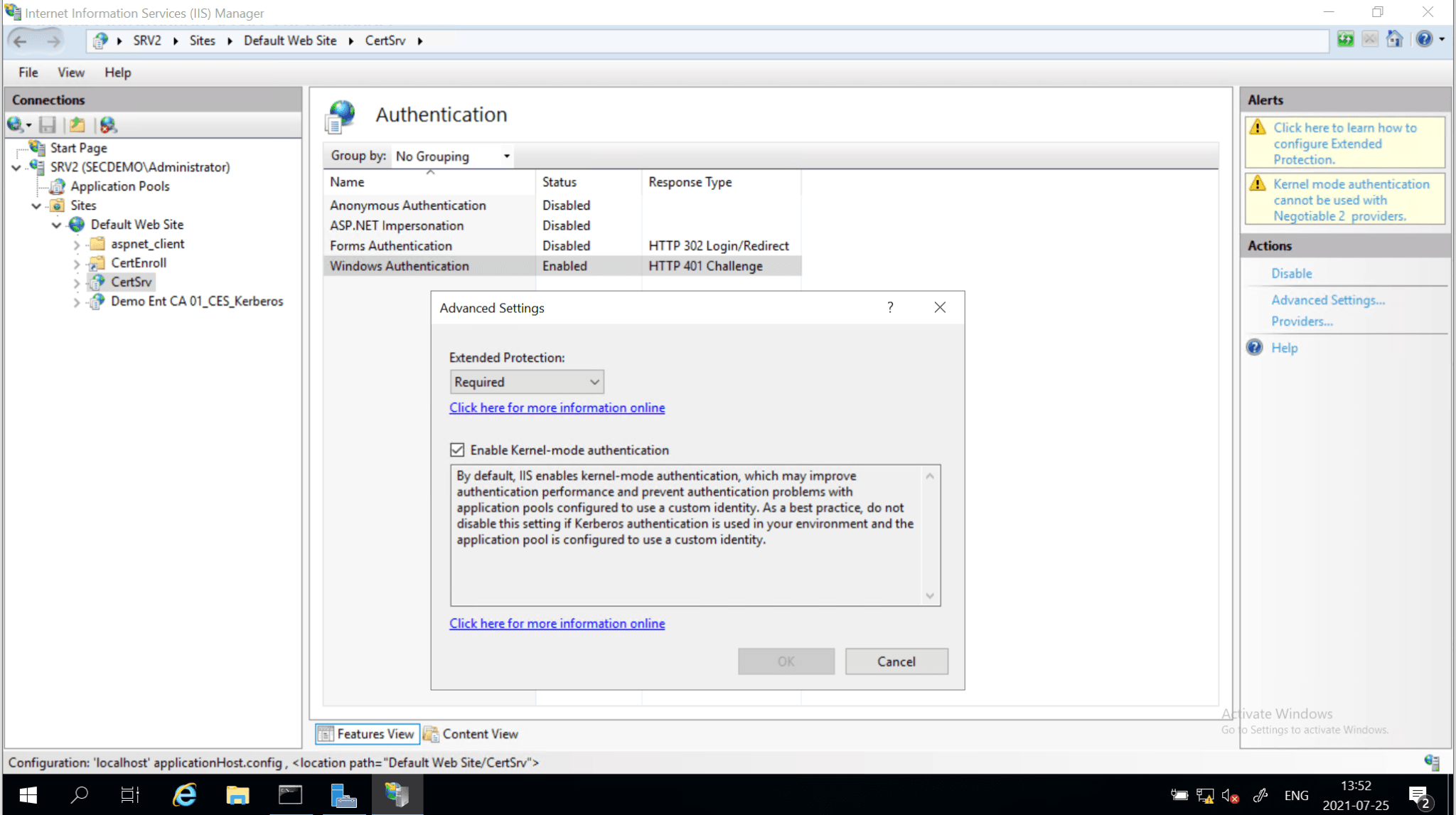
Extended Protection for Authentication (EPA)
- Enable strict network access control to the selected service.
- Always enable TLS for proper transport and session protection.
